
Explore the double declining balance method for depreciation, focusing on calculation, adjustments, and financial reporting insights. Salvage value is the estimated resale value of an asset at the end of its useful life. Book value is the original cost of the asset minus accumulated depreciation.
and Reporting
As the asset’s book value decreases, the depreciation expense also decreases. Since the assets will be used throughout the year, there is no need to reduce the depreciation expense, which is why we use a time factor of 1 balance sheet in the depreciation schedule (see example below). Where you subtract the salvage value of an asset from its original cost and divide the resulting number– the asset’s depreciable base– by the number of years in its useful life. Straight line is the most common method of depreciation, due mainly to its simplicity. Typically, accountants switch from double declining to straight line in the year when the straight line method would depreciate more than double declining. For instance, in the fourth year of our example, you’d depreciate $2,592 using the double declining method, or $3,240 using straight line.
Can you switch to another depreciation method later?
Double declining balance depreciation is a method of depreciating large business assets quickly. Suppose a company purchased a fixed asset (PP&E) at a cost of $20 million. The prior statement tends to be true for most fixed assets due to normal “wear and tear” from any consistent, constant usage. If you want to learn more about fixed asset accounting as a whole, then head to our guide on what fixed asset accounting is, where we discuss the four important things you need to know. Also, if you want to know the other essential bookkeeping tasks aside from fixed asset accounting, you can read our piece on what bookkeeping is and what a bookkeeper does.
Accounts

Consider a scenario where a company leases a fleet of cars for its sales team. These cars are crucial for the business, but they also lose value quickly due to high mileage and wear and tear. Using the DDB method allows the company to write off a larger portion of the car’s cost in the first few years. This higher initial depreciation aligns with the rapid decrease in the car’s value and the heavy use in the early years.
Comparing DDB and Straight-Line Methods

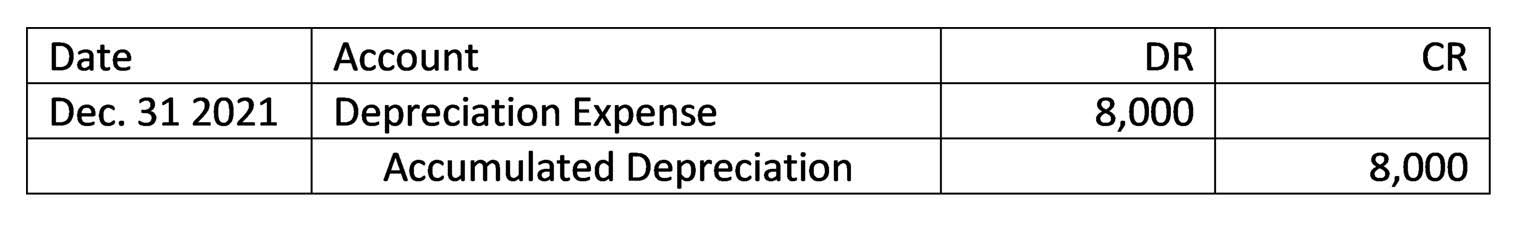
Simultaneously, you should accumulate the total depreciation on the balance sheet. It is advisable to consult with a professional accountant to ensure that depreciation is accurately recorded in compliance with accounting standards and regulations. Under the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) for public companies, expenses are recorded in the same period as the revenue that is earned as a result of those expenses. Sara wants to know the amounts of depreciation expense and asset value she needs to show in her financial statements prepared on 31 December each year if the double-declining method is https://www.bookstime.com/ used. For example, if an asset has a salvage value of $8000 and is valued in the books at $10,000 at the start of its last accounting year.
- These points are illustrated in the following schedule, which shows yearly depreciation calculations for the equipment in this example.
- The current year depreciation is the portion of a fixed asset’s cost that we deduct against current year profit and loss.
- Under the DDB depreciation method, the equipment loses $80,000 in value during its first year of use, $48,000 in the second and so on until it reaches its salvage price of $25,000 in year five.
- As you can see, both methods end up with the same total accumulated depreciation.
- At the beginning of the second year, the fixture’s book value will be $80,000, which is the cost of $100,000 minus the accumulated depreciation of $20,000.
- FitBuilders estimates that the residual or salvage value at the end of the fixed asset’s life is $1,250.
- The DDB method is particularly relevant in industries where assets depreciate rapidly, such as technology or automotive sectors.
- When you use Taxfyle, you’re guaranteed an affordable, licensed Professional.
- Depreciation rates used in the declining balance method could be 150%, 200% (double), or 250% of the straight-line rate.
- When applying the double-declining balance method, the asset’s residual value is not initially subtracted from the asset’s acquisition cost to arrive at a depreciable cost.
However, many firms use a rate equal to 1.5 times the straight-line rate. Under the declining balance method, yearly depreciation is calculated by applying a fixed percentage rate to an asset’s remaining book value at the beginning of each year. An asset for a business cost $1,750,000, will have a life of 10 years and the salvage value at the end of 10 years will be $10,000. You calculate 200% of the straight-line depreciation, or a factor of 2, and multiply that value by the book value at the beginning of the period to find double declining balance method the depreciation expense for that period.

The difference is that DDB will use a depreciation rate that is twice that (double) the rate used in standard declining depreciation. Accountingo.org aims to provide the best accounting and finance education for students, professionals, teachers, and business owners. If the double-declining depreciation rate is 40%, the straight-line rate of depreciation shall be its half, i.e., 20%. Depreciation in the year of disposal if the asset is sold before its final year of useful life is therefore equal to Carrying Value × Depreciation% × Time Factor. No depreciation is charged following the year in which the asset is sold.




